My colleague David Runciman — who is Professor of Politics in Cambridge — had the great idea of doing a weekly podcast from now until the UK has a new government with the aim of holding different kinds of discussions than are possible on mainstream media in the run-up to an election. This week he and I had a long conversation about: whether Facebook could conceivably influence the outcome; about why the current campaign seems so dated (because it seems still to be entirely focussed on ‘old’ media); on why surveillance doesn’t figure as an issue in the campaign; on whether UKIP could be regarded as disruptive in the way that Uber is; and on lots of other stuff.
Spring… honestly!
Straw and Rifkind had nothing to hide, but…
This morning’s Observer column:
The really sinister thing about the nothing-to-hide argument is its underlying assumption that privacy is really about hiding bad things. As the computer-security guru Bruce Schneier once observed, the nothing-to-hide mantra stems from “a faulty premise that privacy is about hiding a wrong”. But surveillance can have a chilling effect by inhibiting perfectly lawful activities (lawful in democracies anyway) such as free speech, anonymous reading and having confidential conversations.
So the long-term message for citizens of democracies is: if you don’t want to be a potential object of attention by the authorities, then make sure you don’t do anything that might make them – or their algorithms – want to take a second look at you. Like encrypting your email, for example; or using Tor for anonymous browsing. Which essentially means that only people who don’t want to question or oppose those in power are the ones who should be entirely relaxed about surveillance.
We need to reboot the discourse about democracy and surveillance. And we should start by jettisoning the cant about nothing-to-hide. The truth is that we all have things to hide – perfectly legitimately. Just as our disgraced former foreign secretaries had.
ISC Chairman had “nothing to hide” but still got into trouble
So Sir Malcolm Rifkind has fallen on his sword after a journalistic sting operation recorded him apparently touting for work from a fake Chinese company that was supposedly wanting him to join its advisory board. The other former Foreign Secretary, Jack Straw, was similarly embarrassed after he was surreptitiously recorded bragging about the access that his status as a former senior minister granted him. Both men protested vigorously that they had done nothing wrong, which may well be true, at least in the sense that they were adhering to the letter of the rules for public representatives.
What’s interesting about Rifkind’s fall is that he used to be an exponent of the standard mantra — “if you have nothing to hide then you have nothing to fear” from bulk surveillance. Both men claim that they had done nothing wrong, but at the same time it’s clear that they have been grievously embarrassed by public exposure of activities that they wanted to keep private. In that sense, they are in the same boat as most citizens. We all do harmless things that we nevertheless regard as private matters which are none of the government’s business. That’s what privacy is all about.
Thinking of Googling for health information? Think again.
Interesting video by Tim Libert, summarising the results of some research he did on the way health information sites (including those run by government agencies) covertly pass information about health-related searches to a host of commercial companies. Libert is a researcher at the University of Pennsylvania. He built a program called webXray to analyze the top 50 search results for nearly 2,000 common diseases (over 80,000 pages total). He found that no fewer that 91% of the pages made third-party requests to outside companies. So if you search for “cold sores,” for instance, and click the WebMD “Cold Sores Topic Overview” link, the site is passing your request for information about the disease along to “one or more (and often many, many more) other corporations”.
According to Libert’s research (Communications of the ACM, Vol. 58 No. 3, Pages 68-77), about 70% of the time, the data transmitted “contained information exposing specific conditions, treatments, and diseases.”
So think twice before consulting Dr Google. Especially if you think you might have a condition that might affect your insurance rating.
The economics of Wolf Hall
As I’ve observed, Peter Kosminski’s wonderful adaptation of Hilary Mantel’s novels has lots of contemporary resonances. In today’s Guardian the paper’s Economics Editor, Larry Elliott, picks up on some of the points the series makes about economics and social mobility. Sample:
What the small screen adaptation can’t really capture from Wolf Hall and the follow-up volume, Bring Up The Bodies, is the book’s broader themes. Mantel’s Cromwell tells us a lot about power and intrigue at the Tudor court. But he also tells us about class, the rise of capitalism and an economy in flux.
The period of transition from feudalism to modern capitalism was long. Economic growth in the 16th century barely kept pace with the growing population. The economy had its ups and down but broadly flatlined between 1500 and 1600. More than two centuries would pass before the advent of the wave of technological progress associated with the start of the industrial revolution.
Even so, the economy was gradually being transformed. Cromwell was not a member of the old aristocratic families: a Suffolk or a Norfolk. He was a blacksmith’s son from Putney made good. Like his patron, Cardinal Wolsey, he did not have a privileged upbringing but had talent and ambition. Karl Marx would have seen Cromwell as a classic example of the new bourgeoisie. Mantel draws a contrast between the fanatically devout Thomas More and the worldly wise Cromwell: the one settling in for a day’s scourging, the other off to get the day’s exchange rate in the City’s Lombard Street, where all the big banking houses had their home.
The inference is clear. Men like More are the past. A new breed of men, pragmatic and servants of the state not the church, are on the rise. “He can converse with you about the Caesars or get you Venetian glassware at a very reasonable rate. Nobody can better keep their head, when markets are falling and weeping men are standing on the street tearing up letters of credit.”
AdvertisementThis, of course, is fiction not fact. But the challenge to the status quo from men like Cromwell was real enough…
A key factor in the story, of course, is the fact that Cromwell was an early Protestant. Elliott goes on to draw on the work of David Landes who argued in The Wealth and Poverty of Nations, that the challenge to the Vatican from the new religion was a major influence because it signified the dawning of a more secular age.
Once he had made Henry supreme over the Church of England and disposed of Anne Boleyn, he set to work on the Dissolution of the Monasteries.
Rather like the privatisation programme of the 1980s, the main reason for the assault on the monasteries was financial: Henry was short of money and wanted the funds to fight his expensive wars. Cromwell could justify what was effectively the enforced nationalisation of church lands by pointing to the corruption of the monastic ideal, but this was of secondary importance.
Nothing really changes. Governments always seem to be short of money. A modern Cromwell charged with sorting out the public finances might conclude that the financial sector – rich, arrogant and with a lamentable record of corruption – was ripe for the picking. No question: if Cromwell was alive today, the former chief executive of HSBC, Stephen Green, would be in chains in the Tower and the Dissolution of the Banks would be in full swing.
Great stuff.
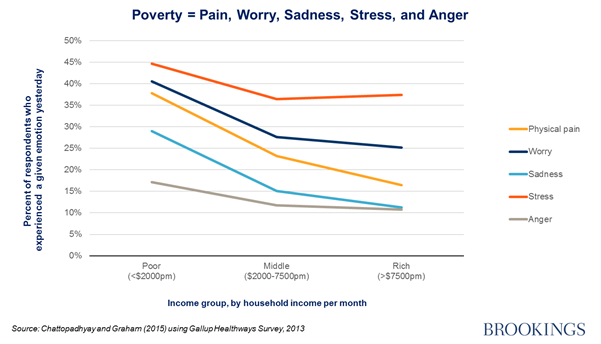
Shock, horror! Being poor is bad for you
Newspapers need editors, not ‘Directors of Content’
Great piece by Peter Preston about the ethical shambles at the Daily Telegraph. Sample:
It’s easy, in such murky circumstances, to lose sight of basic command structures. Much of Fleet Street, indeed, has planted “content” and “strategy” nametags across its digital garden. But the grisly lesson of HSBC is also a fundamental one.
Title inflation may make a paper look cutting-edge digital. It may impress advertisers and investors. It may seem a modern necessity in a world of “native advertising” and fast-flowing revenue streams. But serious newspapers, in whatever form, have a duty of trust: a duty not to be leaned on by pushy politicians, chummy bankers – or advertisers. For how can you put truth first if the truth is for sale?
That’s why the Oborne storm is so deeply damaging. It can’t be put right by appointing some “chief integrity officer”. What the Telegraph lacks, as it stinks and stings under pressure, is what it must now rediscover: a journalist who looks at the likes of HSBC and tells them to get stuffed as and when necessary. A human being, not a corporate assassin. An editor.
Yep.
ALSO: This from Roy Greenslade:
According to Oborne, at a meeting with MacLennan, the CEO was unapologetic about the matter, suggesting that it was no big deal. But it is, of course. It is a very big deal indeed because it goes to the heart of a paper’s credibility. Readers will not trust a newspaper that withholds or censors stories to please advertisers.
Everyone in the newspaper industry knows that advertising is harder and harder to come by. We know also that TMG has been reporting a level of profits for several years that surpasses any other national group. How, we wonder, does it do that?
The implication of Oborne’s revelations is that part of its strategy involves pandering to big advertisers to the extent of curbing critical editorial content.
I imagine this is rare, but once one company gets away with threatening to pull its advertising unless negative stories are pulled then the word goes round. It opens the door to discreet deals. So other instances may have occurred that we know nothing about.
Oborne felt that the HSBC case was so blatant that it was impossible to ignore and it could have far-reaching implications. Frankly, I’m amazed that MacLennan would be party to such activities.
Many people throw mud at him, but there are very few newspaper managers who love the company of journalists as much as he does. He and I have fallen out several times down the years, but I haven’t lost my regard for him. This matter, however, is of a different order altogether.
So what happens next? One theory going the rounds is that the Barclay twins, the owners of the Telegraph, have decided that the way to extract the most value from the paper is to let it go the profitable way of pandering to advertisers, on the grounds that it might last another ten profitable years before it finally collapses under the weight of its own absurdity. So it’s possible they’re not unduly bothered by the fuss about “ethics”.
Technology and Inequality
This morning’s Observer column:
Someone once observed that the difference between Tony Blair and Margaret Thatcher was that whereas Thatcher believed that she was always right, Blair believed not only that he was right but also that he was good. Visitors to the big technology companies in California come away with the feeling that they have been talking to tech-savvy analogues of Blair. They are fired with a zealous conviction that they are doing great stuff for the world, and proud of the fact that they work insanely hard in the furtherance of that goal. The fact that they are richly rewarded for their dedication is, one is given to believe, incidental.
The guys (and they are mostly guys) who manage these good folk are properly respectful of their high-IQ charges. Chief among them is Eric Schmidt, the executive chairman of Google, and a man who takes his responsibilities seriously. So seriously, in fact, that he co-authored a book with his colleague Jonathan Rosenberg on the care and maintenance of these precious beings. Dr Schmidt objects to the demeaning term – “knowledge workers” – that economists have devised for them. Google employees, he tells us, are much, much more impressive than mere knowledge workers: they are “smart creatives”.
In the opinion of their chairman, these wunderkinder are very special indeed…
Terrorism is terrible, sure. We should fight it tooth and nail. But it isn’t an existential threat
One of the many things wrong with the “war on terror” is that it’s a rhetorical device which is used to legitimise all kinds of surveillance activities which, in normal times, would be absolutely verboten in democratic societies. A real state of war is one in which a society faces an existential threat — which is why between 1939 and 1946 the UK was, effectively, a dictatorship in which the government could do anything deemed necessary in order to prosecute the war and confront the threat. In those circumstances, the British people may not have liked many of the things that the government was able to do – which included not just censorship, but also the power to commandeer your house without notice because it was needed for the war effort — but they acquiesced because they understood the nature and the gravity of the threat.
In our time, the threats posed by global terrorism are being used to justify a “state of exception” which looks increasingly like becoming permanent. And the mantra which is incessantly used to justify this is of course the aforementioned rhetorical device. So it’s interesting – and welcome – to hear a major politician explicitly declare that terrorism does not pose an existential threat to our societies. This is what Barack Obama said recently in an interview:
What I do insist on is that we maintain a proper perspective and that we do not provide a victory to these terrorist networks by overinflating their importance and suggesting in some fashion that they are an existential threat to the United States or the world order. You know, the truth of the matter is that they can do harm. But we have the capacity to control how we respond in ways that do not undercut what’s the — you know, what’s essence of who we are.
Spot on. How long, therefore, before the Republicans, primed no doubt by the spooks, begin talking about the US President as a “surrender monkey”. Who knows, maybe the guy even likes French fries?