YouTube turns ten this year. ArsTechnica has a nice post that reflects on its history and its significance.
Excerpt:
The site has become so indispensable that it feels like a basic part of the Internet itself rather than a service that lives on top of it. YouTube is just the place to put videos, and it’s used by everyone from individuals to billion-dollar companies. It’s obvious to say, but YouTube revolutionized Web video. It made video uploading and playback almost as easy as uploading a picture, handled all the bandwidth costs, and it allowed anyone to embed those videos onto other sites.
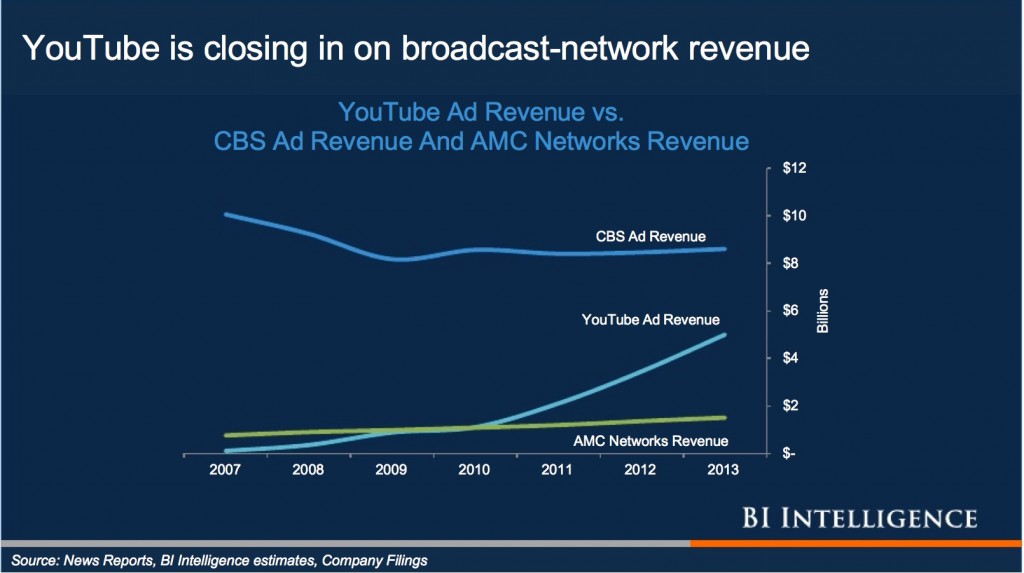
The scale of YouTube gets more breathtaking every year. It has a billion users in 61 languages, and 12 days of video are uploaded to the site every minute—that’s almost 50 years of video every day. The site just continues growing. The number of hours watched on YouTube is up 50 percent from last year.
It’s easy to forget YouTube almost didn’t make it. Survival for the site was a near-constant battle in the early days. The company not only fought the bandwidth monster, but it faced an army of lawyers from various media companies that all wanted to shut the video service down. But thanks to cash backing from Google, the site was able to fend off the lawyers. And by staying at the forefront of Web and server technology, YouTube managed to serve videos to the entire Internet without being bankrupted by bandwidth bills…
Great read. Recommended.