This morning’s Observer column.
So Google has decided to provide end-to-end encryption for any of its Gmail users who wants it. One could ask “what took you so long?” but that would be churlish. (Some of us were unkind enough to suspect that the reluctance might have been due to, er, commercial considerations: after all, if Gmail messages are properly encrypted, then Google’s computers can’t read the content in order to decide what ads to display alongside them.) But let us be charitable and thankful for small mercies. The code for the service is out for testing and won’t be made freely available until it’s passed the scrutiny of the geek community, but still it’s a significant moment, for which we have Edward Snowden to thank.
The technology that Google will use is public key encryption, and it’s been around for a long time and publicly available ever since 1991, when Phil Zimmermann created PGP (which stands for pretty good privacy)…
LATER Email from Cory Doctorow:
Wanted to say that I think it’s a misconception that Goog can’t do targeted ads alongside encrypted email. Google knows an awful lot about Gmail users: location, browsing history, clicking history, search history. It can also derive a lot of information about a given email from the metadata: sending, CC list, and subject line. All of that will give them tons of ways to target advertising to Gmail users – — they’re just subtracting one signal from the overall system through which they make their ad-customization calculations.
So the cost of not being evil is even lower than I had supposed!
STILL LATER
This from Business Insider:
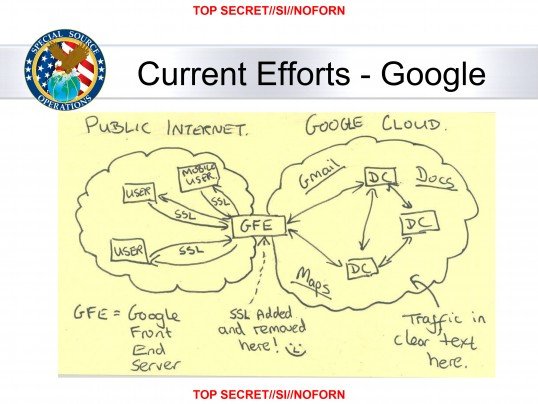
Inside the code for Google’s End-to-End email encryption extension for Chrome, there’s a message that should sound very familiar to the NSA: “SSL-added-and-removed-here-;-)”
Followers of this blog will recognise this as quote from a slide leaked by Edward Snowden.
This comes from a slide-deck about the ‘Muscular’ program (who thinks up these daft names?), which allowed Britain’s GCHQ intelligence service and the NSA to pull data directly from Google servers outside of the U.S. The cheeky tone of the slide apparently enraged some Google engineers, which I guess explains why a reference to it resides in the Gmail encryption code.