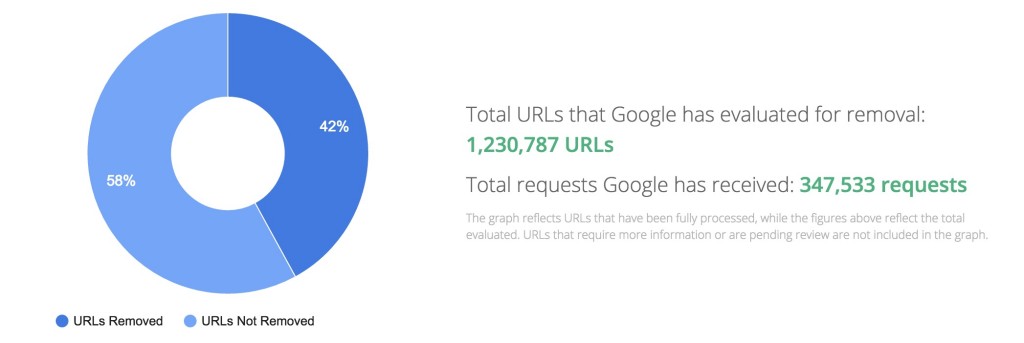
We know that power corrupts. But what about algorithmic power? This morning’s Observer column:
There is a direction of travel here – one that is taking us towards what an American legal scholar, Frank Pasquale, has christened the “black box society”. You might think that the subtitle – “the secret algorithms that control money and information” – says it all, except that it’s not just about money and information but increasingly about most aspects of contemporary life, at least in industrialised countries. For example, we know that Facebook algorithms can influence the moods and the voting behaviour of the service’s users. And we also know that Google’s search algorithms can effectively render people invisible. In some US cities, algorithms determine whether you are likely to be stopped and searched in the street. For the most part, it’s an algorithm that decides whether a bank will seriously consider your application for a mortgage or a loan. And the chances are that it’s a machine-learning or network-analysis algorithm that flags internet or smartphone users as being worthy of further examination. Uber drivers may think that they are working for themselves, but in reality they are managed by an algorithm. And so on.
Without us noticing it, therefore, a new kind of power – algorithmic power – has arrived in our societies. And for most citizens, these algorithms are black boxes – their inner logic is opaque to us. But they have values and priorities embedded in them, and those values are likewise opaque to us: we cannot interrogate them.
This poses two questions. First of all, who has legal responsibility for the decisions made by algorithms? The company that runs the services that are enabled by them? Maybe – depending on how smart their lawyers are.
But what about the programmers who wrote the code? Don’t they also have some responsibilities? Pasquale reports that some micro-targeting algorithms (the programs that decide what is shown in your browser screen, such as advertising) categorise web users into categories which include “probably bipolar”, “daughter killed in car crash”, “rape victim”, and “gullible elderly”. A programmer wrote that code. Did he (for it was almost certainly a male) not have some ethical qualms about his handiwork?