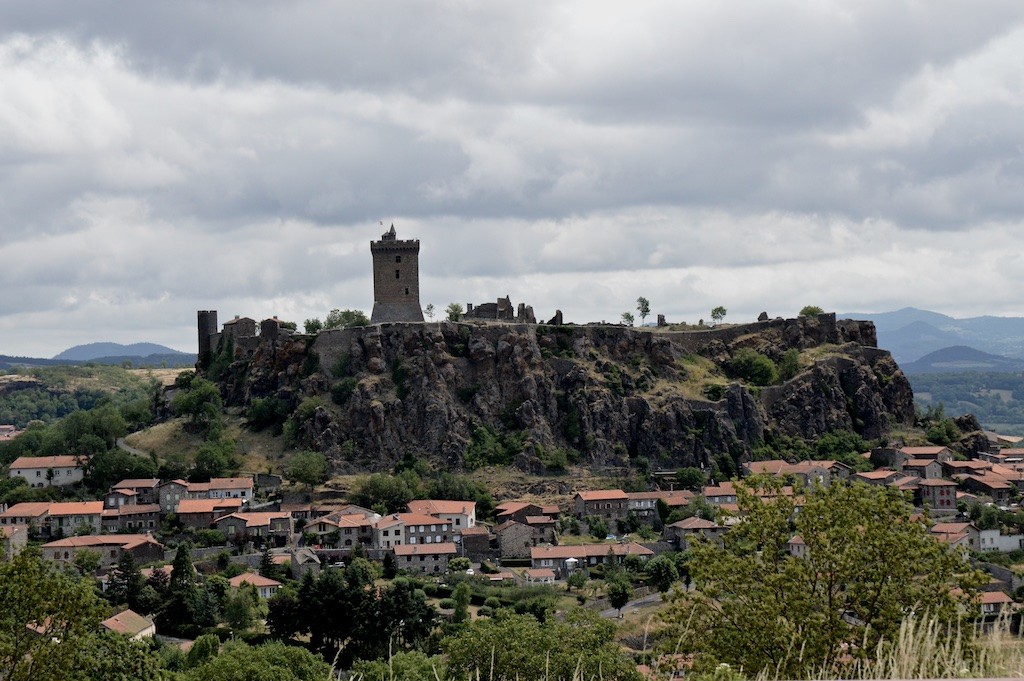
I saw a guy the other day in a Tesla S and was puzzled, because in the past I’ve known him to be a Porsche driver. People who own 911s in particular are notoriously reluctant to change — which is why they tend to be such good customers for dealers. On the other hand, propelling oneself around via a series of controlled explosions — no matter how well-engineered the engine is — is clearly a daft idea in the long run. Electric vehicles are the future. Which, of course, is what Porsche have figured out all by themselves — as the New York Times reports this morning:
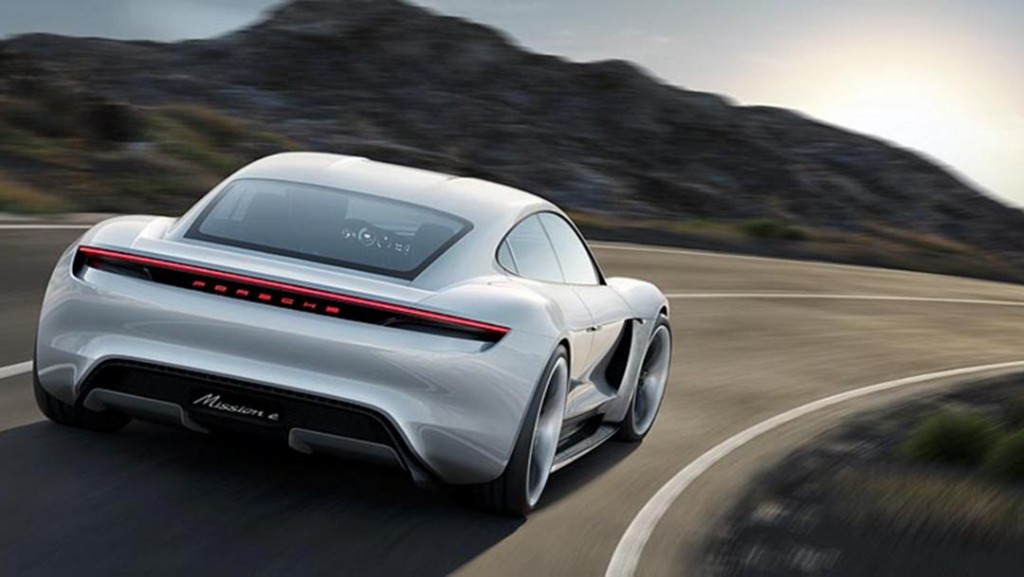
On Monday, at the Frankfurt Auto Show in Germany, Porsche unveiled its all-electric Mission E concept car. A four-door, four-seat luxury performance sedan with futuristic 911 design cues, Mission E will be the first all-electric model Porsche will offer to the public.
Porsche, a German brand, maintains that the vehicle, though it is a concept car, is firmly based in reality and is expected to arrive in showrooms within five years. At the same time, it provides a window into the future of all-electric cars — more range, faster charging and more speed.
With a debut alongside the latest iteration of the classic 911, the Mission E is meant to convey the message that performance and efficiency are not mutually exclusive.
And, for those who really will miss the growl of the 911 engine, I’m sure Porsche can rig up an audio system that produces the same noise electronically.