John Barrow, the Cambridge mathematician (and one of my fellow patrons of the Cambridge Science Festival) has a lovely paper in arXiv. It solves a problem that has always bedevilled competitive rowing — the fact that in an apparently perfectly-balanced coxless boat one still gets a ‘wiggle’ which reduces the efficiency of the team. The Abstract reads:
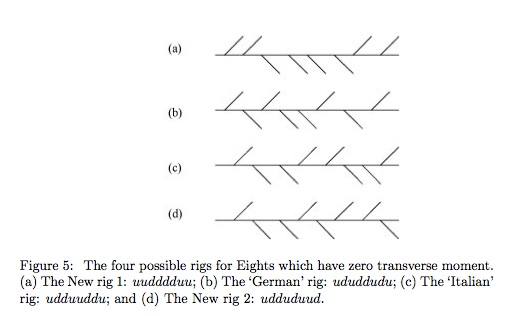
We consider the optimal positioning of an even number of crew members in a coxless racing boat in order to avoid the presence of a sideways wiggle as the boat is propelled forwards through the water. We show that the traditional (alternate port and starboard) rig of racing boats always possesses an oscillating non-zero transverse moment and associated wiggling motion. We show that the problem of finding the zero-moment rigs is related to a special case of the Subset Sum problem. We find the one (known) zero-moment rig for a racing Four and show there are four possible such rigs for a racing Eight, of which only two (the so called ‘Italian’ and ‘German’ rigs) appear to be already known. We also give the 29 zero-moment solutions for racing Twelves but refrain from explicitly listing the 263 Sixteens and 2724 Twenties which have zero transverse moments. We show that only balanced boats with crew numbers that are divisible by four can have the zero-moment property. We also discuss some aspects of unbalanced boats, in which the number of port and starboard oars are unequal.
Isn’t mathematics wonderful? When I was a graduate student, one of my mathematician friends spent three days figuring out the fluid dynamics behind the swirl patterns in his morning coffee. I’m reminded of G.H. Hardy’s lovely book, A Mathematician’s Apology and his famous observation that he had “never done anything ‘useful’. No discovery of mine has made, or is likely to make, directly or indirectly, for good or ill, the least difference to the amenity of the world.”
As you might expect, he was wrong; according to Wikipedia, some of his mathematical work found its way into ‘useful’ applications — e.g. in physics to find quantum partition functions of atomic nuclei (first used by Niels Bohr) and to derive thermodynamic functions of non-interacting Bose-Einstein systems.